XBio:D Javascript Library Reference
Introduction
The XBio:D Javascript library offers the functionality to create rich, dynamic, and interactive features for use with the OJ_Break API. The OJ_Break API provides procedures to retrieve data within the xBio:D database, and the xBio:D JS library is how that data gets presented. Users planning on working with the xBio:D JS library should be familiar with Javascript programming and object-oriented programming.
API Access
All functionality in the xBio:D JS library depends on access of data from the OJ_Break API. See OJ_Break API Access for an overview of the API and how to obtain an API access key.
Example
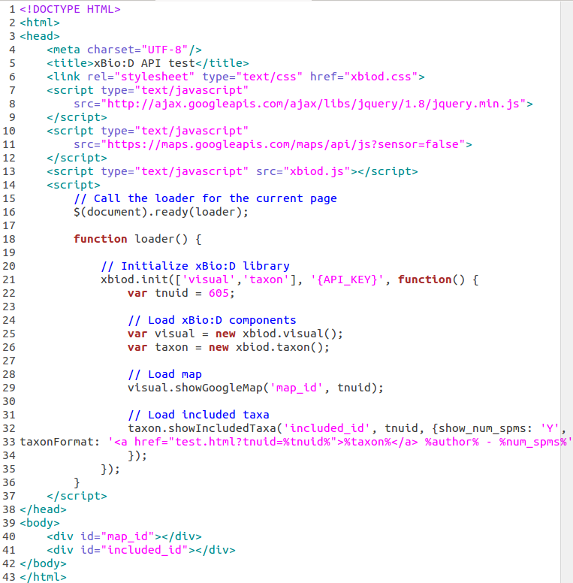
An easy way to become familiar with the xBio:D JS library is to see a simple example involving two web applications. The first is a Google Maps widget which takes data from the OJ_Break method getLocalities for a specified tnuid and displays the data onto an interactive map. Read more about the Google Maps Javascript API here. The second application used in the example is a listing of included taxa for a specified tnuid by using the OJ_Break method getIncludedTaxa (be patient for this method to load).
There are a few things to note about this example:
- The <!DOCTYPE html> tag is necessary for HTML 5 applications (line 1)
- Jquery 1.8 library is included with a <script> tag (line 7 - 9)
- The Map API Javascript is included with a <script> tag (line 10 - 12)
- The xBio:D JS library is included with a <script> tag (line 13)
- In the <body> there are two <div> elements which create areas to hold the widgets. The first is called map_id and the second is included_id. (line 40 - 41)
- Two objects where created to access the xBio:D components called visual and taxon (line 25 - 26)
- The applications are created by calling there respective methods via the xBio:D library components (line 29 & 32 - 33)
These steps will be explained below.